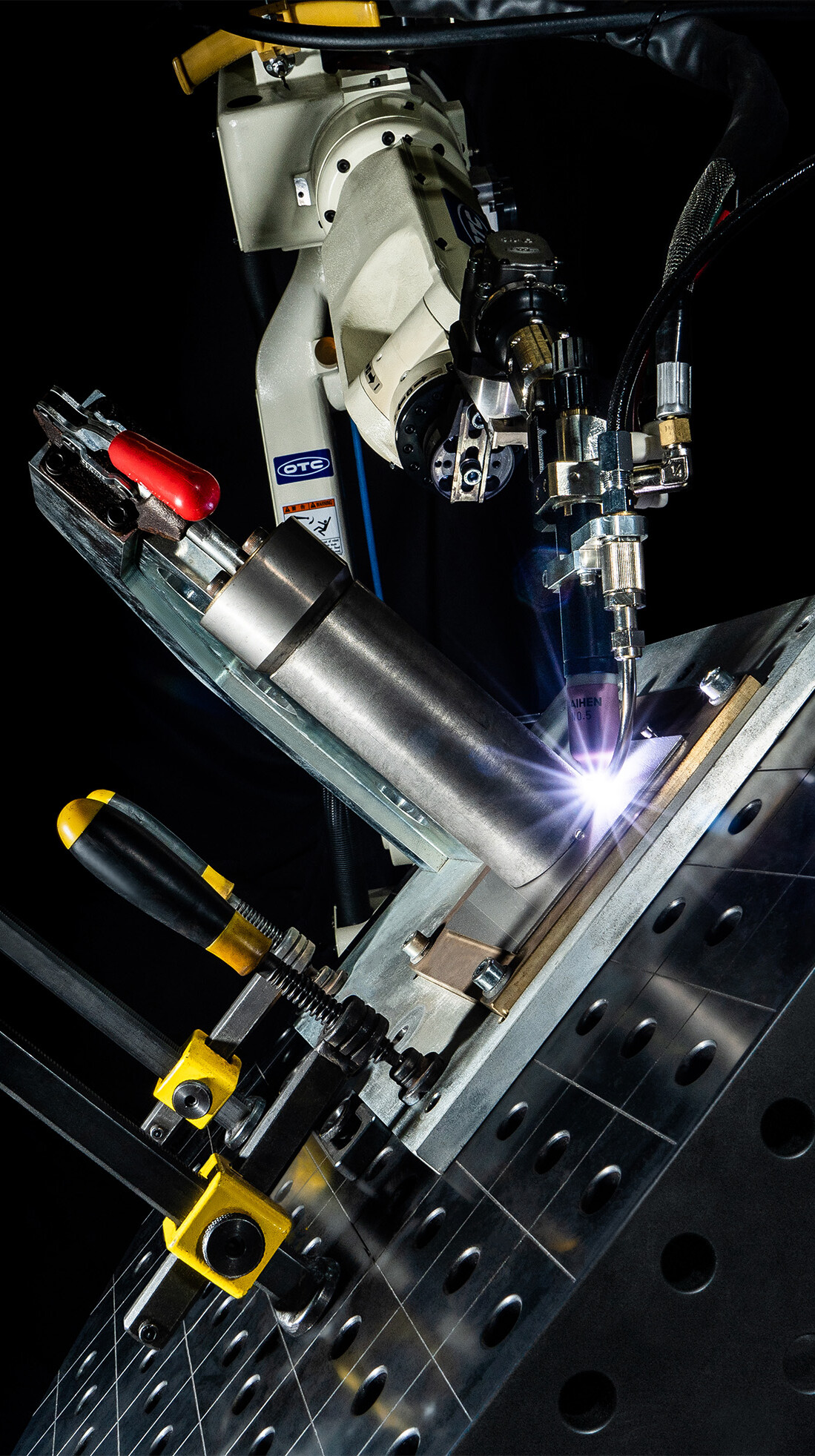
High efficient MIG welding with TIG quality
Our Welbee AC/MIG flagship for manual and robotic welding
The Welbee W400 welding power source is OTC DAIHENs flagship for AC/MIG welding. Main advantages over standard DC pulse welding processes.
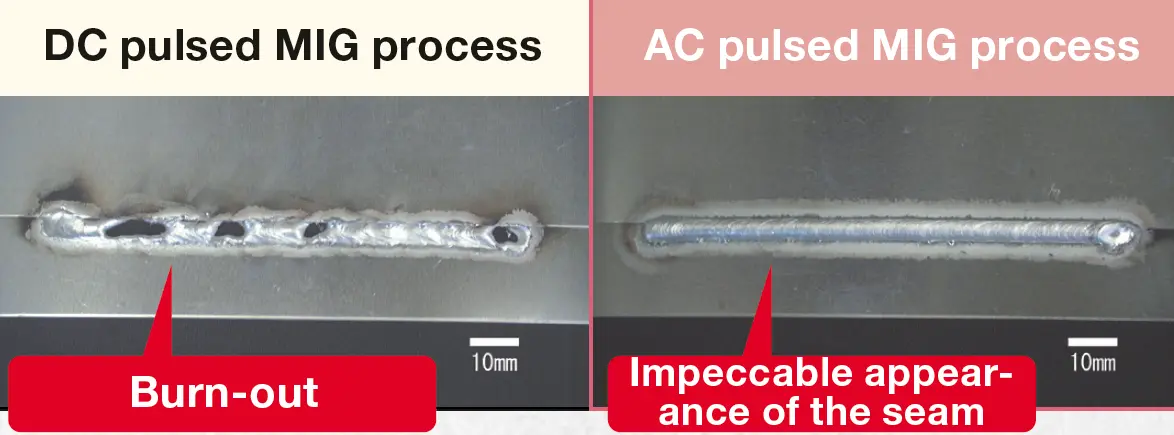
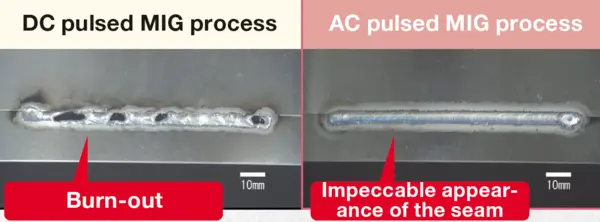
Welding of thin material at high speeds without material distortion
AC/MIG welding is a highly effective welding process that combines two important features: a higher melting rate and an improved penetration control. The increased melting rate at constant current input lowers the heat input into the workpiece. These features make it an ideal choice for welding thin metal sheets up to 0.6 mm in thickness without sacrificing the quality of the weld. AC/MIG welding is applicable for a wide range of materials, including steel, stainless steel, and aluminum.
Improved gab bridging
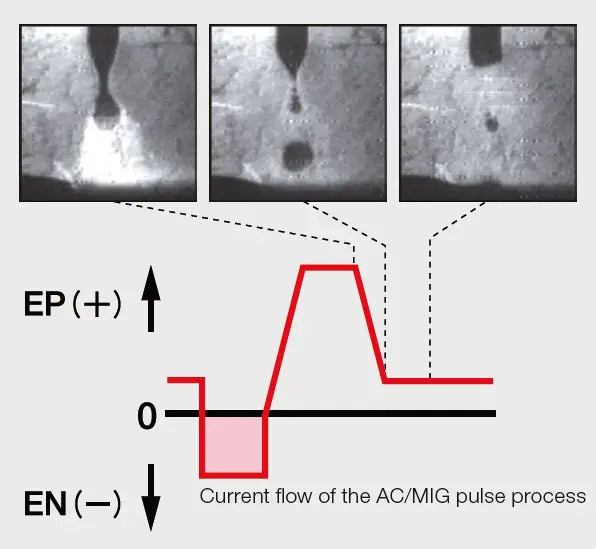
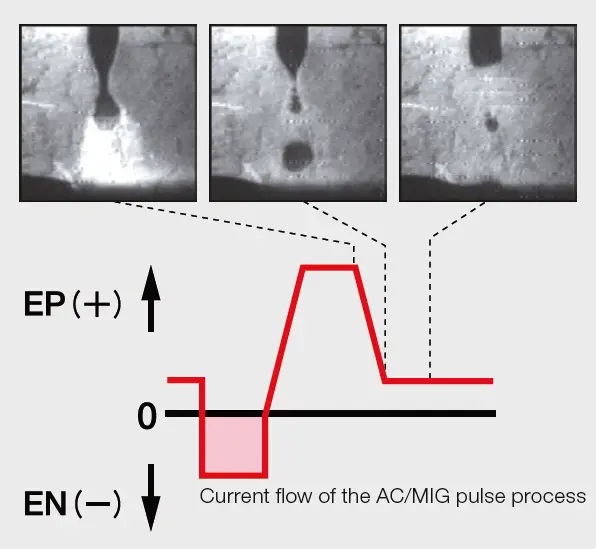
One notable advantage of AC/MIG welding is the flexibility it offers with regard to electrode polarity. In addition to the commonly used positive electrode, known as direct current electrode positive (DCEP), AC/MIG welding allows for the utilization of a negative electrode, referred to as direct current electrode negative (DCEN). This unique feature forms the basis of the welding process, as it involves the alternating current (AC) between DCEP and DCEN.
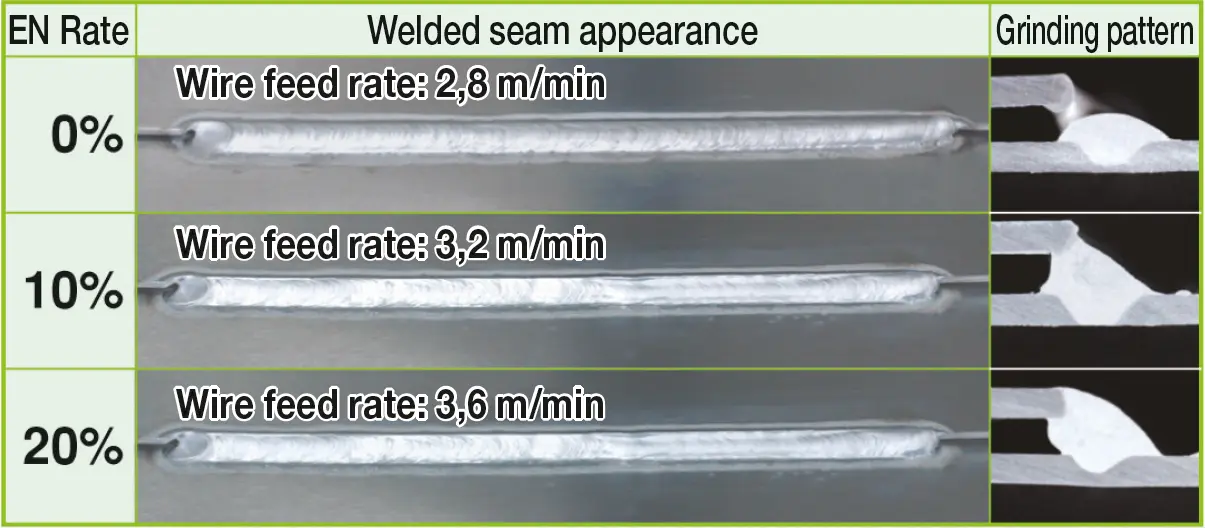


An important aspect influenced by the welding parameters is the EN Ratio, which refers to the proportion of time allocated to the DCEN polarity. By increasing the EN Ratio, there is a corresponding increase in the wire feed rate. Consequently, the higher wire feed rate leads to a greater deposition rate of the welding wire onto the workpiece. This enhanced deposition rate results in an improved capability to bridge gaps between materials during the welding process.
By adjusting the EN Ratio and increasing the wire feed rate, the deposition rate of the welding wire can be heightened, resulting in improved gap bridging capabilities.
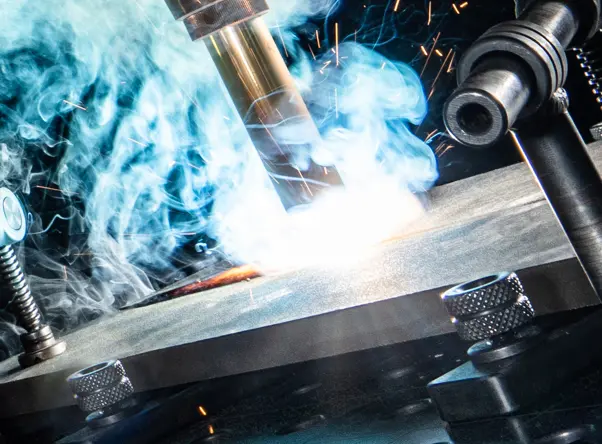


Less welding fumes and oxid layers
AC/MIG welding also offers the benefit of producing less welding fumes and oxide layers. This results in a cleaner weld surface compared to other welding methods. The low temperature required for drop transfer in AC/MIG welding reduces the production of welding fumes. Consequently, there are fewer burn marks and less fume generated during the process. This contributes to a cleaner and visually appealing weld finish.
What is the difference between DC and AC/DC welding?
DC welding is a welding process that utilizes a unidirectional flow of electrical current. In this process, the current flows continuously from the power source to the welding electrode in a single direction. DC welding is commonly employed for welding steel and stainless steel, offering benefits such as better control over the welding pool and deeper penetration.
In contrast, AC/DC welding combines both alternating current (AC) and direct current (DC) in a single welding process. This versatility allows for the flexibility to switch between AC and DC modes.
Nevertheless AC/DC welding machines provide the convenience of switching between AC and DC modes, making them highly versatile for a variety of welding applications. This capability enables welders to work with different materials and adjust the welding process to suit specific requirements.
Discover more